It would be a challenge to think that it only takes a “good” contact with a foreign buyer to start sending your very first pallets to the other side of the world … I can already hear those who say:
“Pfff !!! Yet that’s exactly how it happened for me! ”
I did not say it was not possible, only that if everything went well, you were lucky … I don’t know about you, but I don’t like surprises (well not in my business). I like to prepare myself as much as possible, study everything so as not to find myself stuck in managing a crisis of a container stuck in customs, problems to get paid or productions unable to deliver …
The best way to have this feeling of control (all relative, I can imagine) is to implement a planned export process. This is called international strategic planning.
Developing internationally is expensive and can be complicated! The best attitude to adopt is therefore to move forward in a methodical and organized way.
International strategic planning is very useful because it reduces the risks associated with business development in foreign markets, obtains the necessary financing for its upstream project but alsomore stable sales growth, rather than a “coup” from time to time.
Having an action plan and a planned approach greatly increase a company’s chances of success in foreign markets!
5 steps are needed in order to prepare:
- export diagnosis
- funding search
- standards and certifications
- market research
- Marketing strategy development
1 – Export diagnosis
The very first step in international strategic planning is to carry out an export diagnostic. This will allow the company to know its strengths and weaknesses and assess whether or not it is able to export.
By answering the diagnostic questions, you will objectively discover your company’s level of preparedness for foreign markets, the ability of your teams to absorb excess production and your management’s commitment to international development.
This step is crucial because not all companies are able to export. It is this stage that determines whether your project is feasible or not.
What is an export diagnosis?
A diagnosis is a mapping of your company and your products or services, against the constraints and opportunities of a foreign market.
It has two distinct aspects:
- an internal analysis: the internal diagnosis that will allow you to know the strengths and weaknesses of your own business.
- an external analysis: external diagnosis which will indicate to you the threats and the opportunities of the foreign market
Its achievement within the company
Diagnosis is usually done in two days:
- a day of interviews with your teams and a visit to the premises
- a day of writing the report and the action plan
Of course, the larger the size of the company, the more time it takes to interview the managers of the various departments. We may therefore have to spend more than 2 days in your premises.

We arrive with a grid of questions to ask your service managers: general management, human resources, production, procurement, sales and marketing, innovation and technology, etc.
With the answers collected, we analyze the data to give you an interpretation of your export potential in a report.
The report
The report consists of two parts: the interpretation of the results and the action plan..
3 possible results:
NEGATIVE:
You’re not ready! The weaknesses are too great and the international potential too low. The risk you would be exposing yourself to would be too great-
POSITIF WITH RESERVES:
The company has shortcomings but is surmountable. The action plan will allow you to implement solutions that will allow you to remedy the shortcomings. - POSITIF: The company has no major weaknesses and international potential is high.
We will provide you with the record, an action plan including corrective actions or an international business plan to implement. This action plan will determine the steps to be taken to upgrade and obtain certifications (stage 3 of international strategic planning) and will guide the budget for funding research (stage 2).
2 – Funding search
The decision to export inexorably leads to an increase in the company’s budget. The 2nd step of international strategic planning is therefore financing.
The evaluation of the budget
New spending includes:
- Recruiting an Export Director or Agent or Sales Agent
- investing in market research,
- international marketing costs (prospecting trips, trade shows, etc.)
- une immobilisation financière accrue avec l’augmentation des stocks afin de répondre aux commandes
- Product standards
- obtaining certification
- increase in working capital
- Etc.
The search for funding
Subsidies:
In Canada, there are many programs to finance part of a company’s international development.
The Agri-Food Export Group with its MAPAQ Biofood Export Support (SEB) program or its Agri-Marketing (AAC) program provides more than $100,000 in project funding.
Other federal and/or provincial programs can also help you:
- bring yourself up to standard,
- get the tools you need for international management
- increase your production capacity
- finance your travel abroad
- computerize your industrial process, tools
- Build a webmarketing strategy
- Etc.
We managed, just last year (2019), to get more than $878,000 in grants for 3 clients. Contact us if you want to know if you would be eligible for a grant.
Financial aid from financial institutions:
Factoring is a good way to finance a company’s customer position. It allows for transferring to the financing agency the debt of its client and thus immediately obtain the corresponding cash.
This also helps to limit customer risk since the organization will take guarantees on your client and will only accept the transaction if the customer is solvent (to be sure to be paid in the end).
3 – Standards and certifications
The third stage of international strategic planning is indicated as appropriate in the action plan submitted at the time of the export diagnosis. This will determine whether or not your product requires a standard or certification before being exported.
In the context of an export to Europe, European regulations are so complex that there is a good chance that you will not escape them …
Europe or the country of standards …
European law, which we are particularly familiar with (I have a master’s degree in law from the University of Bordeaux) requires that imported goods meet technical, safety and labeling requirements as defined by European legislation. Before you can reach Europe, your goods must meet EU requirements for the protection of human and animal health, the environment and consumer rights.

These requirements have implications in 6 product categories:
- Sécurité des denrées alimentaires et des aliments pour animaux qui édictent des règles sur la production et la distribution des aliments, l’hygiène, la présence de résidus de pesticides et de contaminants et la traçabilité des produits importés
- la santé animale impose des autorisations du pays exportateur, des agréments d’établissements de transformation et des certificats sanitaires
- la santé végétale impose des certificats phytosanitaires, des inspections et des agréments spécifiques
- la santé publique qui comprend les normes concernant la commercialisation des produits de l’agriculture et de la pêche mais aussi les produits issus de l’agriculture biologique
- product safety that affects cosmetics, industrial products (chemicals, machinery, etc.) and pharmaceutical products
- technical standardization with the famous CE Marking
- les emballages visent à protéger l’environnement et indique la composition des matériaux autorisés
We have devoted a full article on the certification needs of food products, which you can find here: Canada Vs Europe Certifications: What is the real need for businesses?».
Obtaining certification can be long, as mentioned in the article cited above, and can last for months. For example, an ISO 22000 certification takes between 8 and 18 months to implement and obtain.
These delays are incompressible because they include time spent designing and documenting the system, training time for staff, possibly necessary work, and then time for audit and registration.
You can now understand the value of doing good strategic planning internationally. Without it, you would have ended up with products impossible to ship, or worse to have to resume because of not being up to standards or unlicensed …
4 – Study and selection of foreign markets
Market research is essential. It makes it possible to target the markets, to segment prospects which will be used for the development of the marketing strategy.
Between documentary research and field analysis, this study should cover two aspects: a socio-economic and cultural study of the country (custom, partnerships, competition, etc.) and a study of potential clientele (general consumption trends and demographics).
Of course this study is long. It is recommended to limit your choice to 2 or 3 potential markets where your products and services have growth potential.
The country study
Without detailing precisely all aspects of the study of a foreign country, if we had to remember 4, we would say that the most important data to know:
- regulation of international trade and the existence (or lack of) trade agreements,
- the country’s political environment and stability,
- the presence of local or international competitors,
- transport and communication networks
By collecting reliable data on these aspects, you will be able to determine the opportunities and risks presented by these different markets.
The study of potential customers
This is about collecting information about your target audience. Knowing the age, gender, buying habits, place of life, barriers to buying, etc. helps determine a typical profile of a potential buyer.
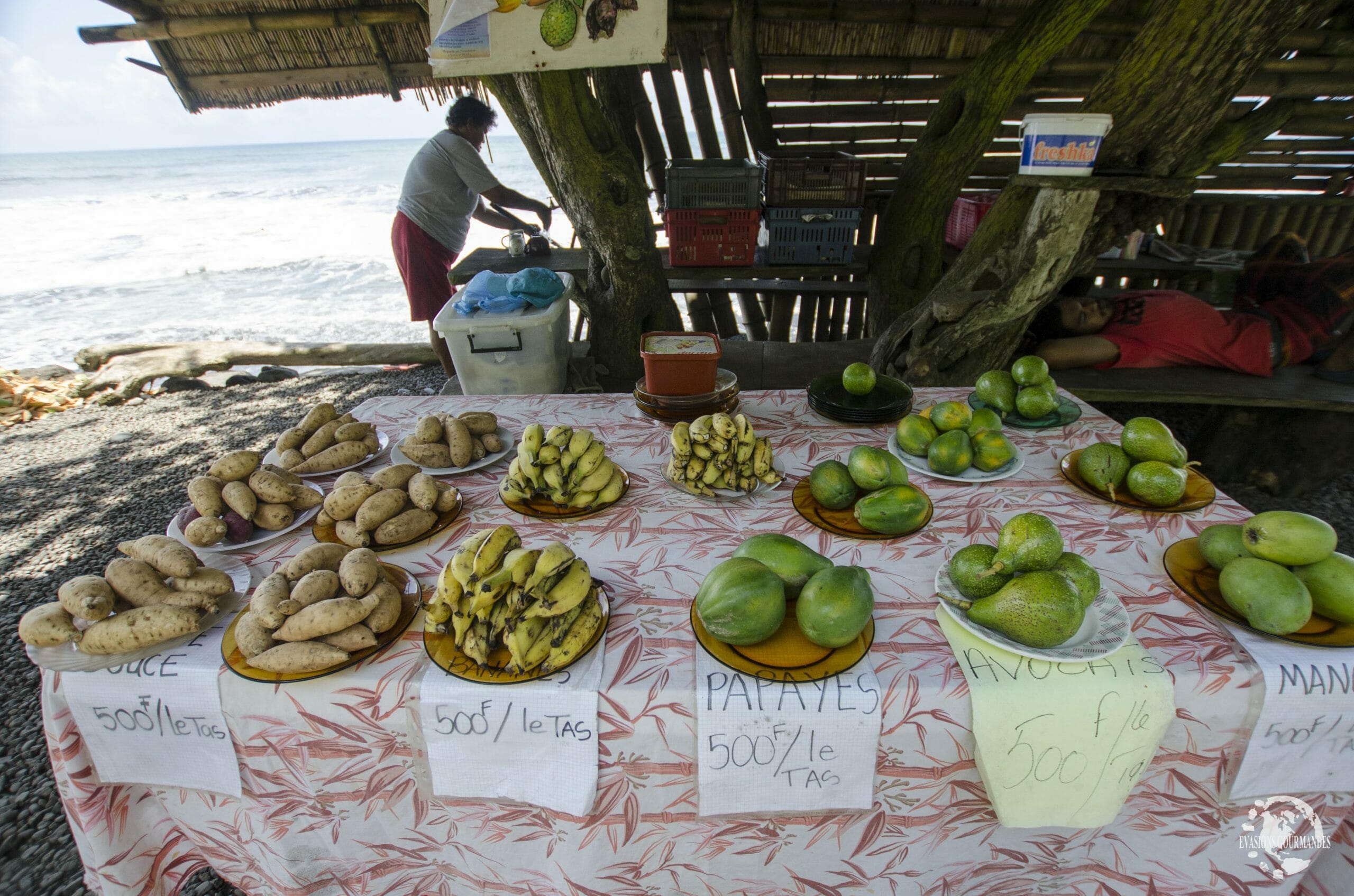

Vegetable sale at a market in Tahiti
Si l’habitude d’achat des consommateurs est d’acheter leurs fruits et légumes dans des marchés locaux, ce n’est peut-être pas la peine d’essayer de les faire venir dans des supermarchés …
The false friend who speaks the common French language increases misunderstandings between the two communities. If we speak the same language, it is a completely different language. This creates considerable barriers to business development in the two respective countries.
We offer training (supported by vocational training) on business culture in France and Canada. Please contact us if you are interested; this can be an ideal springboard for your international growth.
Once the information is gathered, this is where you move to step 5 to adapt your strategy and products to the target market.
5 – Marketing strategy development
Analysis of the data collected helps determine which country is the most interesting for you. It is now necessary now develop the marketing strategy that is the final step in international strategic planning.
What is a marketing strategy?
Simply put, the marketing strategy is how the company wants to implement its policy (or rather its « policies » I mean). There is no one-stop formula because it all depends on your company, your vision and your mission.
These policies are:
- Product policy (product)
- Price policy (price)
- Distribution policy (place)
- Communication policy (promotion)
This is commonly referred to as the “4P” or marketing mixjargon.
This policy that you are going to put in place (or strategy) will allow you to achieve the goals you have set for yourself. Of course you must use the information collected from the market research. You don’t set policies without knowing the context of the market and the clientele you want to reach.
How do you develop your own policies?
Theproduct policy covers all the characteristics of your product.
This is where you will define its positioning (high-end, low-end), its quality, design and appearance, packaging, labelling.
It also includes decisions on enforced warranties, customer service and brands.
The pricing policy refers to the selling price of the product depending on the type of distribution you are going to put in place. So you will have to determine a price based on the quantities ordered or the type of buyer (retailer or importer) which amounts to a bit the same, I grant you …
Discounts and rebates that can be granted to customers will also need to be defined, as will payment, credit, accepted currencies, etc.
The distribution policy concerns the way your products will be distributed. The export diagnostic has given you key information that will allow you to define a distribution method for your products. The manufacturing method of your products and the constraints in terms of storage, delivery, the number of points of sale, etc. are all factors that should help you establish your distribution policy.
The communication policy allows you to give visibility to your product, attract potential customers, close sales and build customer loyalty.
Advertising includes several channels such as websites, social networks, television and the press. But other means are also available such as trade shows and trade fairs. However, these means are more expensive, so they are not given to everyone because they require an investment of time and money. Nevertheless, well prepared, they can prove to be a great tool with a high return on investment.
Our article “International show: for whom? What for? How?Will give you the best steps to prepare yourself and know if it’s right for you.




0 Comments